Search engine is a tool that allows accessing any data such as information, images, news, etc. archived on a subject in digital environments. In a world where information flows non-stop, search engines are our trusted guides in the vast digital world. Have you ever wondered what goes on behind the scenes when you press the search button? Let’s take a journey to demystify search engines and discover how they shape our online adventures.
A search engine is an online tool designed to help users find information on the internet. It works by crawling and indexing web pages and when a user enters a query, it retrieves and displays a list of relevant results. Popular search engines include Google, Bing, and Yahoo, which are essential tools for navigating the vast digital landscape and accessing information efficiently. In essence, a search engine is like a digital compass, helping us navigate the endless maze of information on the internet. But how does it work?
How Search Engines Work?
Behind the scenes, search engines use web spiders, or web crawlers, to explore the internet and build a huge index of information. When you type a query, complex algorithms kick in to sort pages by relevance and quality. Its multifaceted actions, from crawling the entire web to indexing and ranking content, result in a seamless delivery of relevant results. It enriches our online experience by connecting users with the information they are looking for.
When you type a query into a search engine, it performs a seamless retrieval action. It crawls its indexed treasure trove and presents a carefully curated list of results on the Search Engine Results Page (SERP). This personalized digital process, influenced by your previous searches, location and preferences, is what makes search engines an integral part of our daily lives.
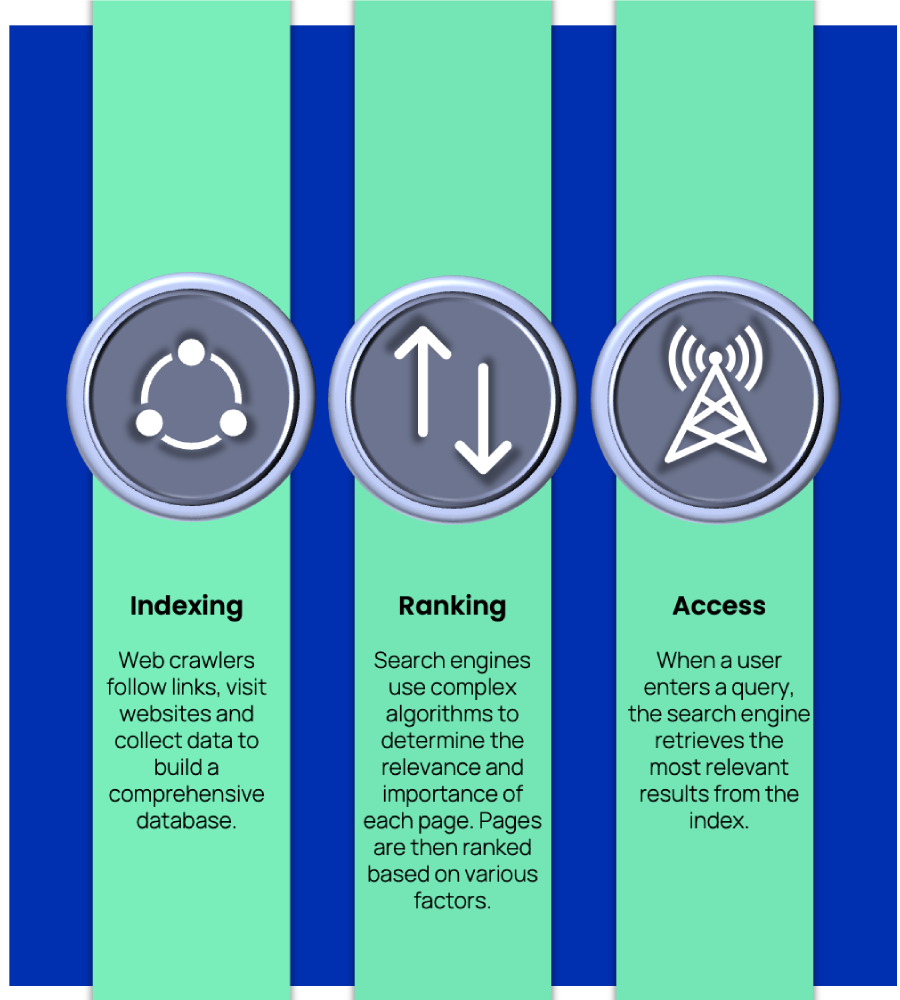
What are the 3 Stages of a Search Engine?
Search engines perform a magical triple task. First, they index the vast networked environment, organizing information like a digital library. Then, algorithms kick in, ranking pages according to various factors. Finally, when you enter a query, the engine quickly retrieves the most relevant results from its indexed treasure trove.
1.Indexing: Search engines use web crawlers to crawl the web and index content. These web crawlers follow links, visit websites and collect data to build a comprehensive database.
2.Ranking: Once the information is collected, search engines use complex algorithms to determine the relevance and importance of each page. Pages are then ranked based on various factors such as keywords, content quality and user experience.
3.Access: When a user enters a query, the search engine retrieves the most relevant results from the index and presents them in an ordered fashion on the search engine results page (SERP).
How are Search Engine Results Ranked?

Imagine search engines as voting hats that evaluate the importance of each web page based on various factors. Keywords, content quality, and user experience all play a role in determining the ranking of pages. Have you ever wondered why some results appear first? It is the complex algorithmic dance between search engines and SEO strategies that decides the ranking.
SEO or Search Engine Optimization. A small but influential part of the digital landscape, SEO plays a key role. It involves optimizing digital content to increase its visibility and ranking in search engines. Imagine it as a secret handshake between your content and search engines to make your information stand out in the digital crowd.
What are the 7 Most Used Search Engines
The digital landscape is dominated by various search engines, led by Google as the global powerhouse, followed by Bing, Yahoo, DuckDuckGo, Baidu, Yandex and AOL Search, each contributing their unique strengths and features to cater to different user preferences and needs. Let’s take a closer look at the features offered by these 7 search engines.
- Google: Google is the most widely used search engine worldwide. It is known for its powerful algorithms that deliver highly relevant search results. Apart from search, Google also offers various services such as Gmail, Google Maps and YouTube.
- Bing: Bing is Microsoft’s search engine designed to compete with Google. It has background images that change daily and offers a wide range of search results. Bing also supports Yahoo Search as part of a partnership.
- Yahoo: Yahoo was one of the first internet giants. Although it has faced challenges, it remains a popular web portal and search engine. Yahoo Search is powered by Bing as part of a partnership between the two companies.
- Yandex: Yandex is the most popular search engine in Russia and the fourth largest in the world. It dominates the search market in Russia and offers various services such as Yandex.Maps, Yandex.Mail and Yandex.Translate.

- DuckDuckGo: DuckDuckGo is a privacy-focused search engine that emphasizes not tracking user data. It has gained popularity as a more private alternative to mainstream search engines. DuckDuckGo does not personalize search results and displays the same results for all users.
- Baidu: Baidu is the dominant search engine in China and is often referred to as the “Google of China”. It offers web search, image search, video search and various other services. Baidu has a significant presence on the Chinese internet.
- AOL Search: AOL (America Online) is an American web portal and online service provider. AOL Search is not as prominent as it used to be, but it still provides search functionality. AOL has undergone several transformations and is now a division of Verizon Communications.
As the Internet continues to evolve, so will the role and capabilities of search engines, providing a unique and enriching online experience for users worldwide. As we complete our search engine journey, it becomes clear that these digital companions are not only gateways to a vast source of information, they also play a pivotal role in shaping our online experiences by influencing the way we explore, learn and connect across the vast internet. So the next time you hit the search button, remember that you’re not just querying a machine; you’re embarking on a personalized exploration with your digital guide.



