A value chain is a set of processes that consists of all the stages from the creation of a company’s product or service to its delivery to the consumer. Since each step in these processes is interconnected, the process is called a value chain. Each link of the chain is connected to the link before and after it. Breaking one of the links means breaking the chain.
For customers, value represents the benefit that the product or service offers them. The greater the benefit, the more valuable the product or service is. For both consumers and trade customers, value is determined by the overall satisfaction derived from a transaction, not by the costs of obtaining it.
Another way of approaching these solutions and benefits is to consider them as (the customer’s) needs. Customers seek to satisfy their needs by purchasing products and services. Meeting needs is therefore a way of delivering value.
How to Implement a Value Chain?
When managing a value chain system, the goal is to optimize the chain to maximize value while minimizing cost. A business has to use value chain activities to create value and then seize that value. The value created by this chain must exceed the sum of the value added by each activity.
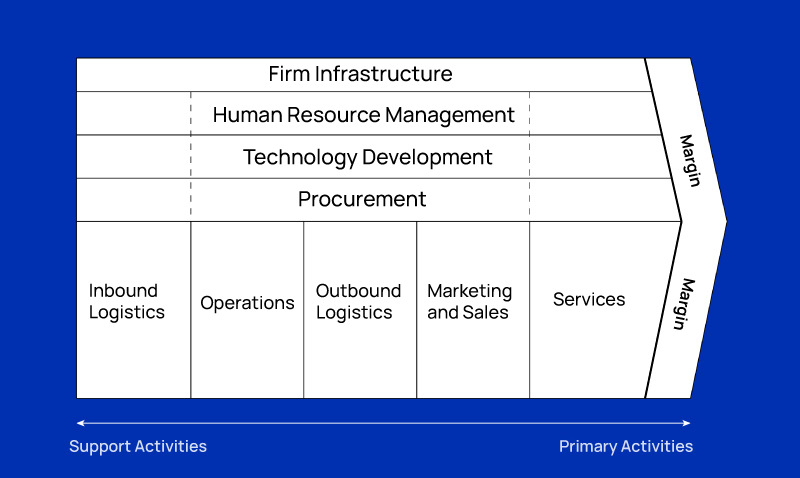
* Porter 1985. Competitive Advantage: Creating and Sustaining Superior Performance by Michael Porter.
Primary activities are the direct actions required to bring materials into an organization, transform them into final products or services, deliver them to customers, and provide marketing and service facilities.
Inbound Logistics: Inbound logistics refers to the company’s main inputs, such as raw materials, purchases, storage and warehouse management.
Operations: It covers the stages of processing the materials in inbound logistics and transforming them into products or services.
Outbound Logistics: Refers to distribution activities, i.e. delivering the product or service to the consumer.
Marketing and Sales: It covers all advertising and marketing activities carried out for the purpose of marketing and promoting the product or service.
Service: Includes after-sales support processes and improvement activities based on feedback.
Support activities facilitate primary activities. For example, purchasing components and materials, hiring appropriately trained employees, and providing and maintaining appropriate technology are important support activities.
Infrastructure: It covers the planning of processes such as planning, accounting and management that constitutes the infrastructure of a company.
Human Resources: The process of recruiting, training and qualifying employees with adequate equipment and skills.
Technology Development: Refers to all development processes carried out by R&D departments of companies.
Supply: It covers the processes through which the company buys its main materials and raw materials.
Management should seek to create value by reducing costs or improving the performance of each activity. But real value is created by linking these activities together through processes in such a way that customers perceive that they are getting superior value. Each of these activities plays an important role in determining the total value of the product or service.

What is the Difference Between Value Chain and Supply Chain?
The idea of a value chain was popularized by American academic Michael Porter in his 1985 book Competitive Advantage: Creating and Sustaining Superior Performance. Although the steps in the value chain are similar to the supply chain, the main purpose of the value chain is for the brand to add its own value at each step. Therefore, in both primary and support activities, the brand should bring its own culture and value to the process.
For example, a bakery that sells bread should choose the best quality flour, yeast and other raw materials by reflecting its own culture even in the first step of providing raw materials. In this way, it will transfer the value of its own brand to the entire production and distribution chain.
In the supply chain, on the other hand, instead of creating a value, it is the correct transfer and sharing of information in the steps starting from raw materials to production and distribution processes.
What the value chain and supply chain have in common is the provision of a quality product or service at low cost. However, the value chain refers to the planning of the supply chain from the beginning with a touch that reflects the brand culture more clearly. Therefore, the supply chain can be seen as a sub-division of the value chain.
Does Value Chain Provide Competitive Advantage?
Competitive advantage means that a company produces its products or services at a lower cost than its competitors for various reasons. Lower cost means more products and therefore more customers. Areas such as raw materials, production, logistics and marketing are the steps where competitive advantage can emerge.
In order for the value chain to provide a competitive advantage, either the value creation activities that take place in the chain must be carried out at low cost or there must be a price that covers the cost of high value creation activities.
The way to find out whether the chain can provide an advantage is to conduct a value chain analysis. Value chain analysis is used to identify at which stages a company can gain a competitive advantage, how it can reduce costs or improve product quality. This analysis can help companies optimize their processes and enhance their competitive position.


