SWOT analysis is a strategic planning tool used to identify the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats of a company, project or any situation. This analysis enables companies to assess both internal and external factors and understand how these factors can affect the organization’s ability to achieve its goals.
The name SWOT analysis comes from the initials for Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats.
Table of Contents
ToggleKey Factors of SWOT Analysis
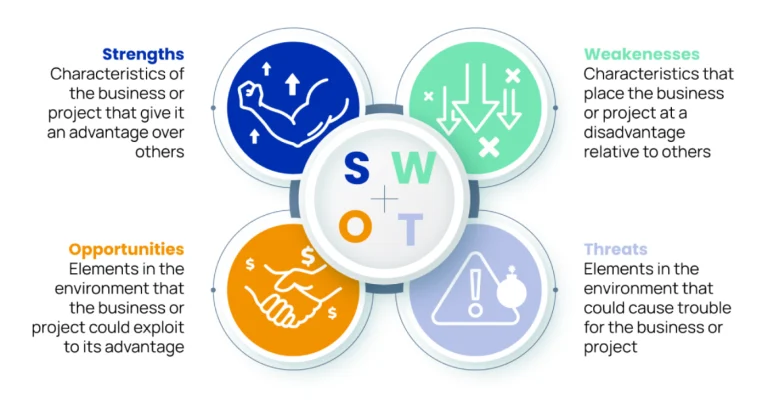
The SWOT analysis consists of four main components:
- Strengths: These are the advantages and resources that the organization has. For example, a strong brand, an experienced employee or an innovative portfolio of products or services.
- Weaknesses: Disadvantages and shortcomings that the organization has. For example, insufficient financing, a weak sales team or an outdated production facility.
- Opportunities: External factors that the organization can take advantage of. For example, the opportunity to enter new markets, the emergence of new technologies or the weakening of competitors.
- Threats: External factors that can affect the organization. For example, economic recession, the emergence of new competitors or changes in consumer preferences.
How to Conduct a SWOT Analysis?
SWOT analysis can be conducted by following the 4 steps below:
- Identify objectives: Before conducting a SWOT analysis, you need to identify the organization’s objectives. These goals can be short-term or long-term, financial or non-financial.
- Assess internal factors: To identify the organization’s strengths and weaknesses, assess internal factors. These factors include the resources, capabilities, skills and processes that the organization has.
- Assess external factors: To identify the organization’s opportunities and threats, assess external factors. These factors include economic, social, political and technological factors in the environment in which the organization operates.
- Evaluate the results: Use the results of the SWOT analysis to develop the organization’s strategy.
When conducting a SWOT analysis, the answers to the following questions should be sought and a strategy path should be drawn based on these answers:
- What are the advantages and disadvantages of competitors? Which aspects do other companies see as superior to their own?
- What needs to change, what are the shortcomings?
- Which factors reveal weaknesses, where does the company stagnate?
- What are the opportunities in the service area? What kind of innovations and changes would make business simpler?
Finding the right answers allows companies to diversify their success stories. For companies, achieving something also gives them the responsibility to assume a certain role in the modern market. It is worth accompanying your company on this path of responsibility and identifying strategies that will yield the right results in the long term, rather than short term plans.
Benefits of SWOT Analysis
SWOT analysis can provide companies with the following benefits:
- It helps companies understand their strengths and weaknesses.
- It helps companies identify opportunities and threats.
- Helps companies develop their product/service/market strategies.
- Help companies use their resources more efficiently.
- Helps companies reduce internal and external risks.
Why Use SWOT Analysis?
SWOT analysis can be used in various ways to help companies develop strategies.
A company can use SWOT analysis to:
- Develop strategies for entering new markets.
- Develop strategies for new products or services.
- Develop strategies to monitor the actions of its competitors.
- Develop marketing
- Develop financial strategies.
SWOT analysis is a powerful strategic planning tool for businesses. This analysis can help businesses understand their competitiveness and position in the market and increase their chances of success.
Disadvantages of SWOT Analysis
It is necessary to assess the disadvantages as well as the advantages:
- SWOT analysis is based on past information. Therefore, it may not fully reflect future developments.
- SWOT analysis is a subjective technique. The results of the analysis may vary according to the opinions of the analyzer.
- SWOT analysis is static. It assesses the company’s internal and external environment at only a point in time. This analysis may not help the company adapt to its ever-changing environment.
Examples of SWOT Analysis
Technology Company
Strengths
- Strong financial performance.
- High-quality products and services.
- Strong customer loyalty and brand recognition.
- Ability to invest in innovation and technology.
Weaknesses:
- High operational costs.
- Limited international market presence.
- Lack of efficiency in business processes.
- Training needs of the sales team.
Opportunities:
- Opportunities to expand into new markets.
- Expanding product portfolio by following industry trends.
- Opportunities to establish strategic collaborations and partnerships.
- Evaluating digital marketing and e-commerce opportunities.
Threats:
- Strong competition.
- Economic uncertainties.
- Regulations and changes.
Software Project
Strengths
- Experienced and specialized employees in the project team.
- Ample financial support and budget.
- Well-established project planning and management process.
- A strong stakeholder and cooperation network.
Weaknesses:
- Lack of communication between resources.
- Uncertainties in the project process.
- Insufficiently experienced employee.
- Uncertainty in setting strategic objectives.
Opportunities:
- Opportunities to develop products to meet market demands.
- Opportunities to update project context by closely following industry trends.
- Opportunities for strategic partnerships and sponsorship.
- Opportunities to integrate new technologies into the project.
Threats:
- Unanticipated cost overruns during the project.
- Difficulty adapting to rapid changes in the market.
- Financial difficulties of cooperating partners.
- Risk of loss of market share due to competition.
SWOT analysis is an important strategic planning tool for companies. This analysis can help the company identify its strengths and weaknesses, opportunities and threats, and understand how these factors may affect the organization’s ability to achieve its goals and, with this information, improve its strategy, use its resources more efficiently and reduce risks.



